akonadi_next
Some classes to be merged into akonadi when finished. This doc will also need to be merged.
How to use Akonadi in your application
This library provides classes for KDE applications to communicate with the akonadi server. The most high-level interface to Akonadi is the Models and Views provided in this library. Ready to use models are provided for use with views to interact with a tree of collections, a list of items in a collection, or a combined tree of Collections and items.
Collections and Items
In the Akonadi concept, Items are individual objects of PIM data, eg emails, contacts, events, notes etc. The data in an item is stored in it a typed payload. For example, if an Akonadi Item holds a contact, the contact is available as a KABC::Addressee:
Additionally, an Item must have a mimetype which corresponds to the type of payload it holds.
Collections are simply containers of Items. A Collection has a name and a list of mimetypes that it may contain. If a collection may contain events if it can contain the mimetype 'text/calendar'. All Collections have the same mimetype. A Collection which can itself contain Collections must be able to contain the Collection mimetype.
This systems makes it simple to create PIM applications. For example, to create an application for viewing and editing events, you simply need to tell akonadi to retrieve all items matching the mimetype 'text/calendar'.
Models and Views
Akonadi models and views are a high level way to interact with the akonadi server. Most applications will use these classes.
Models provide an interface for viewing, deleting and moving Items and Collections. New Items can also be created by dropping data of the appropriate type on a model. Additionally, the models are updated automatically if another application changes the data or inserts of deletes items etc.
Akonadi provides several models for particular uses, eg the MailModel is used for emails and the ContactsModel is used for showing contacts. Additional specific models can be implemented using EntityTreeModel as a base class.
A typical use of these would be to create a model and use proxy models to make the view show different parts of the model. For example, show a collection tree in on one side and show items in a selected collection in another view.
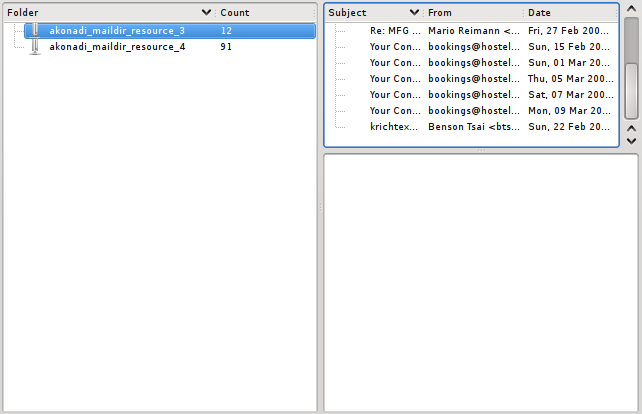
- Warning
- Some of the features in the examples below are not fully implemented yet. See entitytreemodel.h for a list of remaining issues with the api and implementation of these classes.
The content of the model is determined by the configuration of the Monitor passed into it. The examples below show a use of the EntityTreeModel and some proxy models for a simple heirarchical note collection. As the model is generic, the configuration and proxy models will also work with any other mimetype.
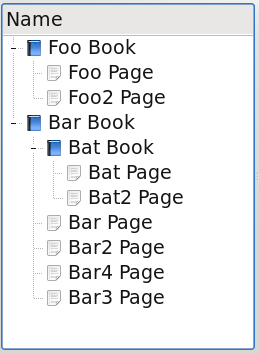
The EntityTreeModel can be further configured for certain behaviours such as fetching of collections and items.
To create a model of only a collection tree and no items, set that in the model. This is just like CollectionModel:
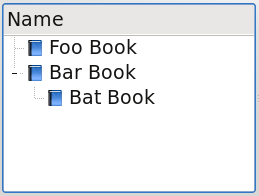
Or, create a model of only items and not child collections. This is just like ItemModel:
The CollectionModel-like and ItemModel-like configurations will probably not be used much. Usually, a full tree of collections and items will be created and proxy models will be used to filter collections or items as needed.
Or, to create a model which includes items and first level collections:
The items in the model can also be inserted lazily for performance reasons. The Collection tree is always built immediately.
Additionally, a DescendantEntitiesProxyModel may be used to alter how the items in the tree are presented.
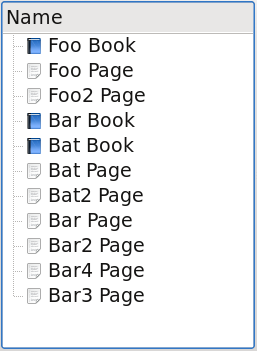
DescendantEntitiesProxyModel can also display the same data as FlatCollectionProxyModel, but optionally for the entire entity tree, not just collections.
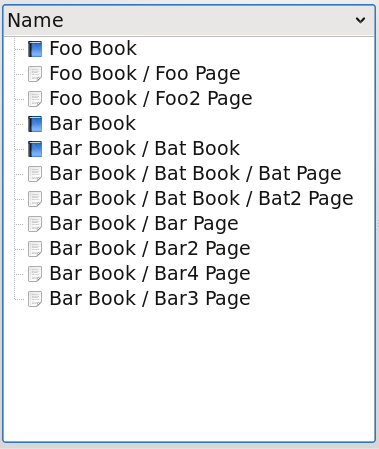
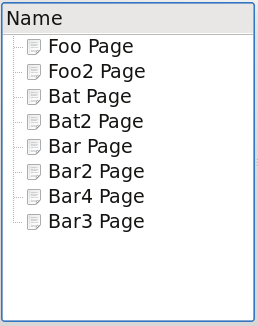
This proxy can be combined with a filter to for example remove collections.
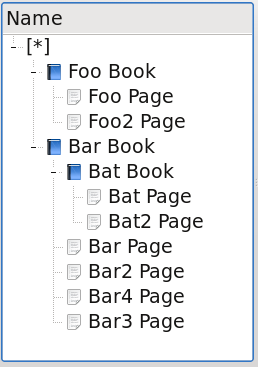
It is also possible to show the root item as part of the selectable model:
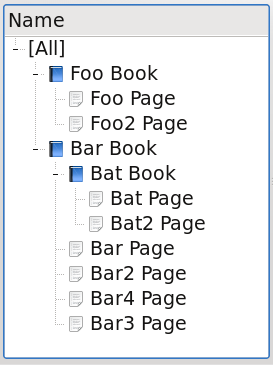
By default the displayed name of the root collection is '[*]', because it doesn't require i18n, and is generic. It can be changed too.
These can of course be combined to create an application which uses one EntityTreeModel along with several proxies and views.
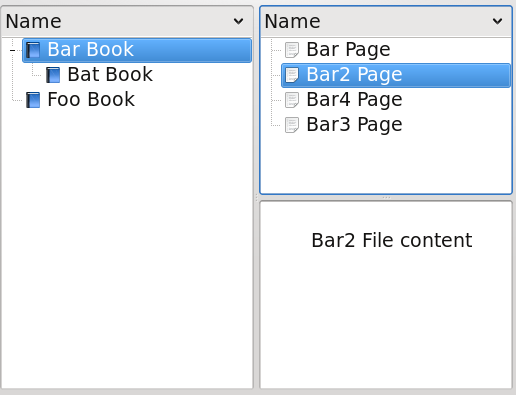
Or to also show items of child collections in the list:
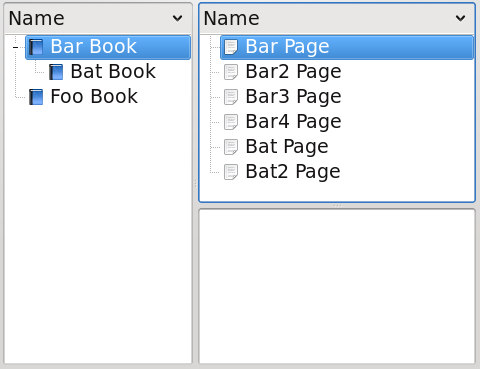
Note that it is important in this case to use the DescendantEntitesProxyModel before the MimeTypeFilterProxyModel. Otherwise, by filtering out the collections first, you would also be filtering out their child items.
A SelectionProxyModel can be used to simplify managing selection in one view through multiple proxy models to a representation in another view. The selectionModel of the initial view is used to create a proxied model which includes only the selected indexes and their children.
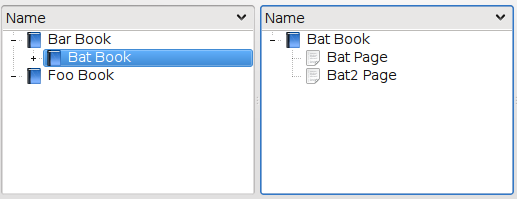
The SelectionProxyModel can handle complex selections.
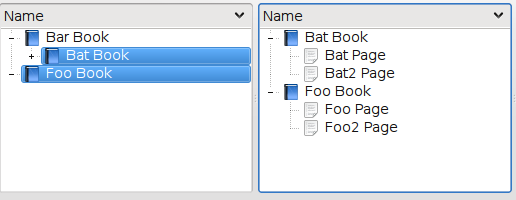
If an index and one or more of its descendants are selected, only the top-most selected index (including all of its descendants) are included in the proxy model. (Though this is configurable. See below)
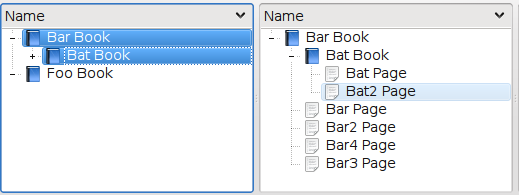
SelectionProxyModel allows configuration using the methods setStartWithChildTrees, setOmitDescendants, setIncludeAllSelected. See testapp/proxymodeltestapp to try out the 5 valid configurations.
Obviously, the SelectionProxyModel may be used in a view, or further processed with other proxy models. See the example_contacts application for example which uses a further DescendantEntitiesProxyModel and MimeTypeFilterProxyModel on top of a SelectionProxyModel.
The SelectionProxyModel orders its items in the same top-to-bottom order as they appear in the source model. Note that this order may be different to the order in the selection model if there is a QSortFilterProxyModel between the selection and the source model.
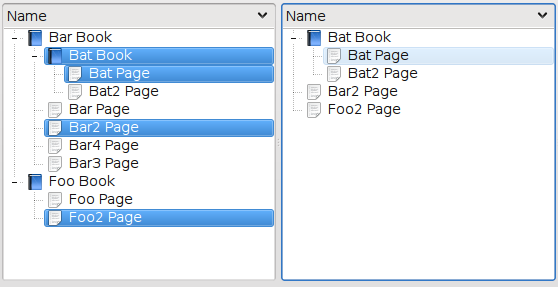
A different view can also be used with the model, such as a QColumnView. However this does not work because QColumnView does not listen to signals from the model (http://www.qtsoftware.com/developer/task-tracker/index_html?id=246999&method=entry).
Work is also started on time based proxy models so that Items containing calendar data can be represented in a table.
Jobs and Monitors
The lower level way to interact with Akonadi is to use Jobs and Monitors (This is what models use internally). Jobs are used to make changes to akonadi, and in some cases (eg, a fetch job) emit a signal with data resulting from the job. A Monitor reports changes made to the data stored in Akonadi (eg, creating, updating, deleting or moving an item or collection ) via signals.
Typically, an application will configure a monitor to report changes to a particular Collection, mimetype or resource, and then connect to the signals it emits.
Most applications will use some of the low level api for actions unrelated to a model-tree view, such as creating new items and collections.
Tricky details
Change Conflicts
It is possible that while an application is editing an item, that item gets updated in akonadi. Akonadi will notify the application that that item has changed via a Monitor signal. It is the responsibility of the application to handle the conflict by for example offering the user a dialog to resolve it. Alternatively, the application could ignore the dataChanged signal for that item, and will get another chance to resolve the conflict when trying to save the result back to akonadi. In that case, the ItemModifyJob will fail and report that the revision number of the item on the server differs from its revision number as reported by the job. Again, it is up to the application to handle this case.
This is something that every application using akonadi will have to handle.
Using Entity::Id as an identifier
Items and Collections have a id() member which is a unique identifier used by akonadi. It can be useful to use the id() as an identifier when storing Collections or Items.
However, as an item and a collection can have the same id(), if you need to store both Collections and Items together by a simple identifier, conflicts can occur.
In this case, it makes more sense to use a normal qint64 as the internal identifier, and use the sign bit to determine if the identifier refers to a Collection or an Item. This is done in the implementation of EntityTreeModel to tell Collections and Items apart.
Unordered Lists
Collection and Item both provide a ::List to represent groups of objects. However the objects in the list are usually not ordered in any particular way, even though the API provides methods to work with an ordered list. It makes more sense to think of it as a Set instead of a list in most cases.
For example, when using an ItemFetchJob to fetch the items in a collection, the items could be in any order when returned from the job. The order that a Monitor emits notices of changes is also indeterminate. By using a Transaction however, it is sometimes possible to retrieve objects in order. Additionally, using s constructor overload in the CollectionFetchJob it is possible to retrieve collections in a particular order.
Be careful when fetching collections recursively
Collections could be returned in multiple signal calls and out of order.
: more info.
Resources
The KDEPIM module includes resources for handling many types of PIM data, such as imap email, vcard files and vcard directories, ical event files etc. These cover many of the sources for your PIM data, but in the case that you need to use data from another source (for example a website providing a contacts storage service and an api), you simply have to write a new resource.
http://techbase.kde.org/Development/Tutorials/Akonadi/Resources
Serializers
Serializers provide the functionality of converting raw data, for example from a file, to a strongly typed object of PIM data. For example, the addressee serializer reads data from a file and creates a KABC::Addressee object.
New serializers can also easily be written if the data you are dealing with is not one of the standard PIM data types.
Implementation details
Updating Akonadi Models
- Note
- The details here are only relevant if you are writing a new view using EntityTreeModel, or writing a new model.
Because communication with akonadi happens asynchronously, and the models only hold a cached copy of the data on the akonadi server, some typical behaviours of models are not followed by Akonadi models.
For example, when setting data on a model via a view, most models syncronously update their internal store and notify akonadi to update its view of the data by returning true.
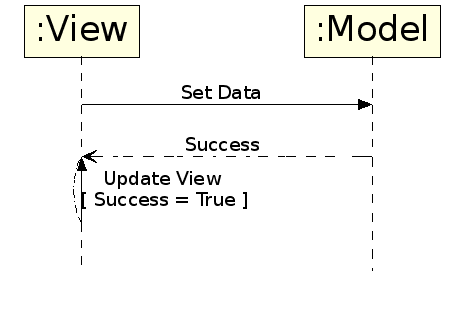
Akonadi models only cache data from the akonadi server. To update data on an Akonadi::Entity stored in a model, the model makes a request to the akonadi server to update the model data. At that point the data cached internally in the model is not updated, so false is always returned from setData. If the request to update data on the akonadi server is successful, an Akonadi::Monitor notifies the model that the data on that item has changed. The model then updates its internal data store and notifies the view that the data has changed. The details of how the Monitor communicates with akonadi are omitted for clarity.
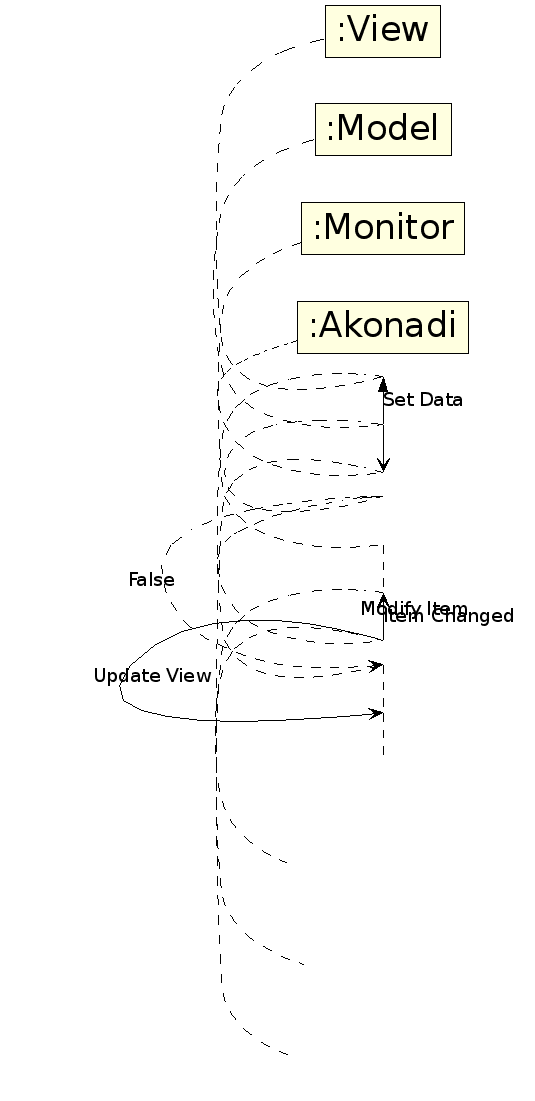
Similarly, in drag and drop operations, most models would update an internal data store and return true from dropMimeData if the drop is successful.
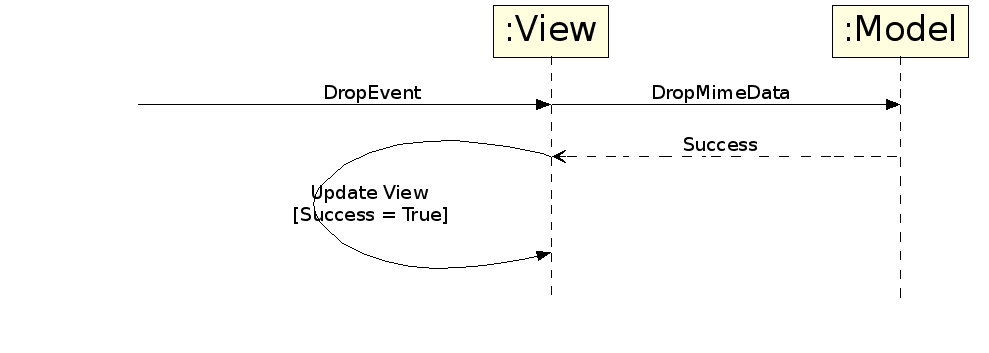
Akonadi models, for the same reason as above, always return false from dropMimeData. At the same time a suitable request is sent to the akonadi server to make the changes resulting from the drop (for example, moving or copying an entity, or adding a new entity to a collection etc). If that request is successful, the Akonadi::Monitor notifies the model that the data is changed and the model updates its internal store and notifies the view that the model data is changed.
Documentation copyright © 1996-2014 The KDE developers.
Generated on Tue Oct 14 2014 22:54:57 by doxygen 1.8.7 written by Dimitri van Heesch, © 1997-2006
KDE's Doxygen guidelines are available online.
 KDE API Reference
KDE API Reference