MauiKit Calendar
Introduction
MauiKit Calendar is a set of QtQuick components and classes for visualizing calendar dates and creating events. The visual controls are designed to integrate well with the rest of MauiKit controls and the Maui HIG. Part of the back-end solutions used by this framework are based on Akonadi by the KDE community.
You can think of this - and other - MauiKit Frameworks as KDE's KParts, where each module accomplishes a specific function and when plug together you can quickly assemble a more powerful app. Components like this one are usually used and shared among multiple Maui Applications.
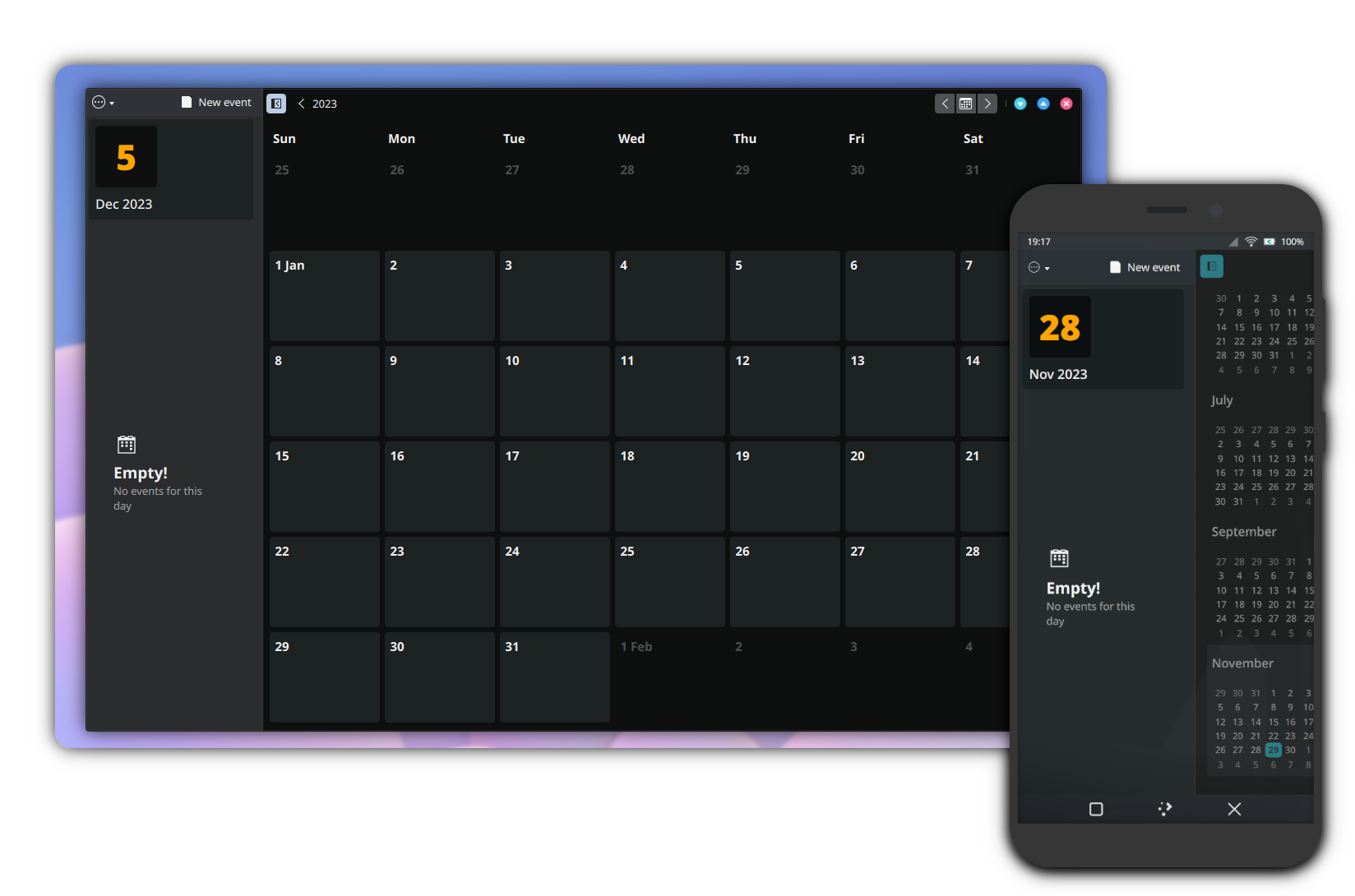
Components
MauiKit Calendar has a set of visual controls and helper classes. Some of the visual controls are a graphical representation of the classes or wrappers that consume the API models.
Visual Controls
Classes
The helper classes contain models andcontrollers for interfacing with the file system.
Minimal Example
Tutorial
To use this framework components, you can import the module using QML as import org.mauikit.calendar, or include the headers and link to the target library for C++.
Examples for every control can be found in the examples directory.
If you have any questions about MauiKit Calendar, feel free to drop by the Maui Project group on Telegram as [at]mauiproject.
A complete guide on how to set up and create an application using the MauiKit Calendar controls can be found here quickstart.
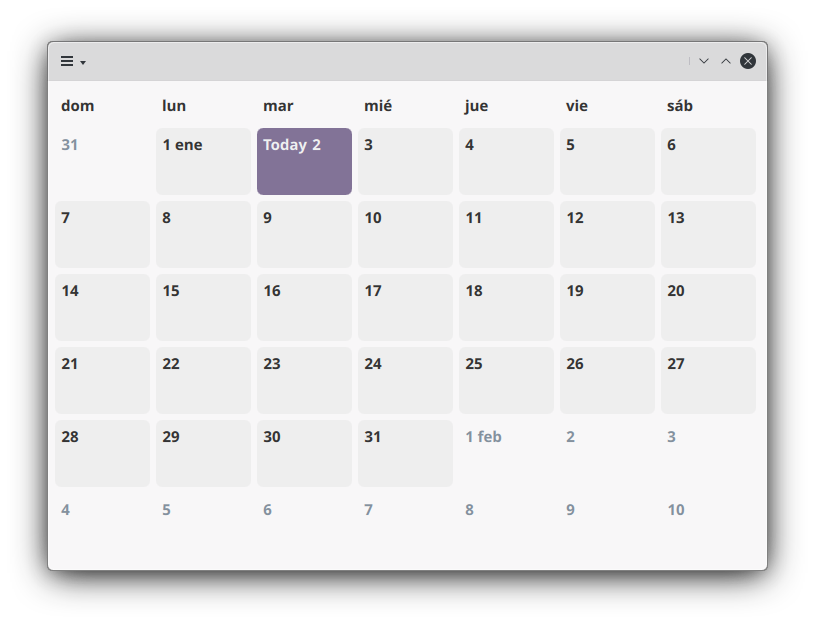
Deployment
Building
For building MauiKit Calendar from source, you will need to be familiar with some basic shell commands, with a console aka terminal emulator and your distribution package manager.
Before building it, make sure you have all the dependencies already installed with its development files.
git cmake make kf6-ki18n kf6-kcoreaddons qt6-svg qt6-base mauiman4 mauikit4 kpim6-akonadi-mime-dev kpim6-akonadi-mime libkf6akonadicontact6 libkf6akonadicontact-dev kpim6-calendarsupport kpim6-akonadi-contacts-dev libkpim6calendarsupport-dev
Then you can clone the project to your machine.
git clone https://invent.kde.org/maui/mauikit-calendar.git
Now that you have the sources, go into the mauikit-calendar folder and start the building process.
cd mauikit-calendar
Let's build the project into a separate directory
mkdir build
Then.
cd build
An lets build it. In this example the installation prefix path is set to the /usr directory; you can modify it if you want to, but bare in mind that you will also need to let know Qt where else it can find the installed QML plugins.
cmake .. -DCMAKE_INSTALL_PREFIX=/usr -DBUILD_WITH_QT6=ON
If everything goes right, the next step is to install it on the system for it to be ready to be used.
Installation
Once the project has been built from source - as explained in the previous section, you can install it.
sudo make install
This step will install the QML plugin to the right location.
If you don't want to build it from source, you can also look for it in your distribution packages.
For example, to install it on Arch based distributions:
sudo pacman install mauikit-calendar
Debian based distros:
sudo apt install mauikit-calendar4
For Android, you will need to build it from source and install it at your Qt for Android root directory.
The easiest way is to build it using Qt Creator. Go to the project settings page, and enable the CMake build step for installation. That will install MauiKit into the right location. Remember you need to set the Kit to be Android. You can read more about setting up Qt from Android on their website.
Usage
The simplest and recommended way to use MauiKit is to just use the packages provided by your Linux distribution, or build it as a module and deploy it together with the main application.
Once MauiKit has been installed you can start using it in your QML files. Checkout the ApplicationWindow for a quick example.
Examples
Android
Notes
Contributing
If you find any syntax errors, missing documentation, or not working code snippets or examples, please consider reporting the issue at MauiKit Calendar issues page, with the documentation tag.
If you want to contribute with the documentation efforts, you can contact the Maui Project at Telegram [at]mauiproject.
- Maintainer(s)
- Camilo Higuita <milo..nosp@m.h@ao.nosp@m.l.com.nosp@m..com>
Documentation copyright © 1996-2025 The KDE developers.
Generated on Fri May 2 2025 12:01:13 by doxygen 1.13.2 written by Dimitri van Heesch, © 1997-2006
KDE's Doxygen guidelines are available online.